Investigation of the plasmonic effect in air-processed PbS/CdS core–shell quantum dot based solar cells†
Abstract
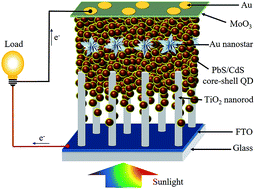
Integrating appropriate plasmonic nanostructures into colloidal quantum dot (QD) based solar cells is an attractive strategy for improving their power conversion efficiency (PCE). Such manipulation allows enhanced photon absorption by QDs and, therefore, more charge carrier generation. In this work, we report the investigation of plasmon enhanced bulk heterojunction solar cells involving Au nanostars incorporated into a near infrared PbS/CdS core–shell QD film spin coated onto TiO2 nanorod arrays. The rationale behind choosing the Au nanostars is based on their balance of light scattering and strong near field, which allows coupling to the surrounding QD film, as supported by finite-difference time-domain calculations. The effect of the density and location of the Au nanostars in the QD film on device performance was studied in detail and optimal parameters were identified. Following such parameter optimization, a PCE of 4.16% has been achieved, which was about 16% higher than that (PCE: 3.59%) of the control device without Au nanostars. This increase in the PCE was found to be mainly due to the increase in short circuit current (Jsc) (about 26% in this case), suggesting that the presence of Au nanostars enhances the charge carrier generation via improving photon absorption. This was further confirmed by the enhancement of the photoresponse as evidenced by the increase of external quantum efficiency mainly in the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) spectral region of the Au nanostars. Theoretical calculations were first carried out to simulate back reflection, absorption, and extinction as well as the local electric field distribution around the Au nanostar embedded in the QD film. These primary calculations then served as a basis for theoretically assessing the contributions from scattering and near field to absorption enhancement as a function of the location of the Au nanostar within the QD film by taking into consideration five simultaneously occurring processes in the solar cell. Correlating the experimental and calculation results clearly suggests that enhanced Jsc and PCE of the solar cells involving the Au nanostars are due to enhancement of absorption via both the near field and scattering effects, with the former being the dominant factor.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2016 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...