Molybdate flux growth of idiomorphic Li(Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3)O2 single crystals and characterization of their capabilities as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
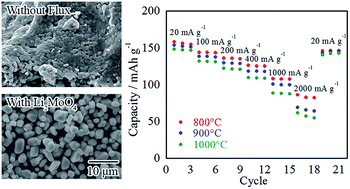
A Li2MoO4 flux enabled size-tunable idiomorphic Li(Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3)O2 (NCM) crystal growth. The crystal size was controlled from 0.26 to 4.4 μm simply by changing the experimental conditions (i.e., solute concentration and reaction temperature). The obtained crystals individually dispersed in both water and N-methylpyrrolidone without unexpected agglomeration; however, Li deficiency and a thin amorphous-like layer formed on the NCM crystal surface during flux removal with water. We found that post-heat-treatment with LiOH significantly improved the discharge capacity of NCM. Recovery of the surface quality of the NCM crystals was primarily responsible for the capacity improvement. The electrodes achieved a high capacity of 81 mA h g−1 under a high current density of 2000 mA g−1, while the electrodes prepared from commercially available NCM showed a maximum of 65 mA h g−1. The rate and cycle performance of the flux-grown NCM crystals was highly dependent on the crystal size. Smaller crystals showed excellent discharge capacities at high C rates, whereas larger crystals showed better cycle performances.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...