Limits on anion reduction in an ionically functionalized fullerene by cyclic voltammetry with in situ conductivity and absorbance spectroscopy
Abstract
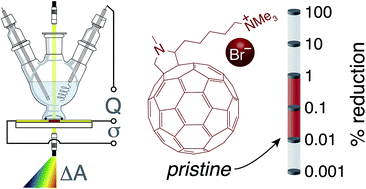
Electron selective interfacial layers are necessary for the production of efficient organic and lead halide perovskite solar cells. Recently it has been asserted that ion-containing fullerene-based interfacial layers with high conductivities are self n-doped by anion reduction. In this study, dual-electrode spectroelectrochemistry is employed to determine the relationship between reduction level, conductivity, and in conjunction with absorbance spectroscopy the initial level of reduction of films of an ion containing fullerene, N,N,N-trimethyl-5-(N-methyl-3,4-[60]fulleropyrrolidin-2-yl)pentan-1-aminium bromide (NMFP-Br). We calculate an extinction coefficient at λmax of 5 × 103 M−1 cm−1 and a maximum conductivity of 6.1 × 10−2 S cm−1 at 40% of maximum reduction. We determine that anion-induced reduction is not occurring to a significant extent in pristine films of NMFP-Br. We also observe that the conductivity of electrochemically reduced NMFP-Br is consistent with a mixed-redox conduction mechanism. These results, with consideration of commonly reported conductivities and mobilities, are useful in understanding why ion-containing fullerene films are initially highly conductive.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...