A conductive polymer coated MoO3 anode enables an Al-ion capacitor with high performance†
Abstract
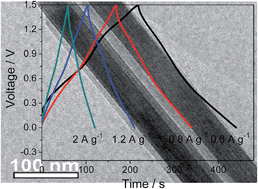
Electrochemical capacitors are becoming promising energy conversion/storage and power output devices. However, high cost and low energy density are two serious disadvantages. By integrating the advantages of Li-/Na-ion batteries and electrochemical capacitors, Li-/Na-ion capacitors have been explored recently. Al is very cheap and is the most abundant metal element on the earth. There are few reports on Al-ion capacitors due to the challenges in finding a suitable anode with large capacitance and good rate performance. Here, the feasibility of assembling an Al-ion capacitor with good electrochemical performance is demonstrated. The Al-ion capacitor is assembled by using a composite of MoO3 nanotubes coated by a conductive polypyrrole (PPy@MoO3) as an anode, which functions via a redox intercalation/deintercalation of Al3+ ions in aqueous solution. It delivers a capacitance of 693 F g−1, about 3 times higher than that of electrode materials for sodium-ion capacitors in aqueous solution. Combined with an activated carbon (AC) cathode, the Al-ion capacitor presents an energy density of 30 W h kg−1 and an excellent cycling life with 93% capacitance retention after 1800 cycles. This finding provides another energy storage device with low cost and promotes the application of capacitors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...