A catalyst-free amorphous silicon-based tandem thin film photocathode with high photovoltage for solar water splitting†
Abstract
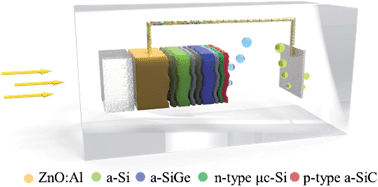
Nowadays, efficient production of storable clean hydrogen from abundant and sustainable solar energy is increasingly being identified as an essential route to realize the future sustainable hydrogen energy. Here we demonstrate a p-type amorphous silicon carbon (a-SiC:H) protected amorphous silicon/amorphous silicon germanium (a-Si/a-SiGe) tandem photocathode that is highly promising to realize a stable, large-scale, and efficient solar water splitting device. Our studies show that by electrically lossless coating a p-type a-SiC:H protection layer on an a-Si/a-SiGe tandem thin film solar cell with a preceding n-type narrow-gap μc-Si:H layer to improve the electron transfer, a high photocurrent onset potential can be achieved for the protected a-Si/a-SiGe tandem photocathode. In comparison to reported intrinsic a-SiC:H protection layers and n-type layers in a-Si/a-SiGe tandem cells, the proposed p-type a-SiC:H protection layer shows a better hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) catalytic activity, which is comparable to amorphous molybdenum sulfide (a-MoS3) catalyzed unprotected a-Si/a-SiGe tandem photocathodes even without any HER catalyst. Combined with the hybrid photoelectrode concept, this stable photocathode with high photovoltage is highly promising to form a wireless, highly stable, and efficient monolithic solar water splitting device for hydrogen production.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...