A high energy density Li-rich positive-electrode material with superior performances via a dual chelating agent co-precipitation route†
Abstract
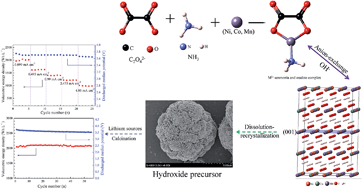
A new Li-rich positive-electrode Li1.13(Ni0.26Co0.09Mn0.52)O2 is successfully achieved via a dual ammonia and oxalate chelating agent co-precipitation route for the first time, which delivers a high volumetric energy density of over 2100 W h L−1, superior cycle life and stable high median-voltage. The dual or multiple chelating agent method gives a new insight towards high energy density for Li-rich materials with outstanding electrochemical performances for advanced lithium-ion batteries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...