Highly sensitive H2S detection sensors at low temperature based on hierarchically structured NiO porous nanowall arrays†
Abstract
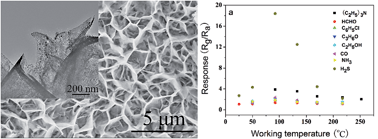
3D network-like, hierarchically structured, porous nanowall NiO arrays were grown in situ on ceramic tubes by a facile but environmentally friendly hydrothermal reaction with a subsequent calcination process. The arrays were constructed of the interconnected porous nanosheets, which were further assembled with abundant nanoparticles. The gas-sensing properties of such porous nanowall NiO array film sensors were investigated with eight inorganic and organic gases. The H2S-sensing performance was observed to be in a large dynamic range (1 ppb to 100 ppm) and the lowest detection limit was 1 ppb at 92 °C compared with other reported oxide-based sensors. The sensor exhibited not only high sensitivity, good selectivity and reproducibility to H2S with resistance to humidity at a low temperature of 92 °C and room temperature, but also good linear relationship under concentration ranges of ppm level (1–100 ppm) and ppb level (1 ppb to 1 ppm). The excellent sensing performance of this array film sensor to H2S could be ascribed to the porous structures in the unique nanowall arrays with a large specific surface area, which benefit H2S molecules to adsorb/desorb onto/from the array surface as well as the electron transfer. The formation of NiO arrays and their possible H2S-sensing mechanism are discussed in detail.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...