Encapsulating sulfur into a hybrid porous carbon/CNT substrate as a cathode for lithium–sulfur batteries†
Abstract
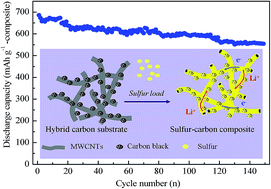
A hybrid carbon substrate as a sulfur immobilizer is obtained via simple processes to fabricate cathode materials for lithium–sulfur batteries. The microstructure and morphology of the sulfur/carbon composites are characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). It is demonstrated that commercial carbon black and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in the hybrid substrate cooperate well with each other in an appropriate mass ratio. In particular, a large sulfur content of 81.7 wt% can be loaded into the hybrid carbon substrate forming the sulfur/carbon composite. When the mass ratio of carbon black and CNTs is 1 : 1, the composite delivers a high initial capacity of 837.3 and 685.9 mA h g−1(composite) at the current densities of 80 and 160 mA g−1(composite) when used as a cathode-active material. The discharge capacity remains at 554.4 mA h g−1(composite) at a current density of 160 mA g−1(composite) after 150 cycles, indicating a low capacity fading of about 0.12% per cycle. Besides, the composite offers a high Coulombic efficiency of about 100%. The significant improvements in the electrochemical performance are associated with the desirable combination of carbon black and CNTs in the hybrid carbon substrate. Therefore, this work proposes a low-cost and effortless approach to prepare sulfur/carbon composites with high performance as cathodes for lithium–sulfur batteries.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2015 Journal of Materials Chemistry A Hot Papers

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...