Metal and F dual-doping to synchronously improve electron transport rate and lifetime for TiO2 photoanode to enhance dye-sensitized solar cells performances†
Abstract
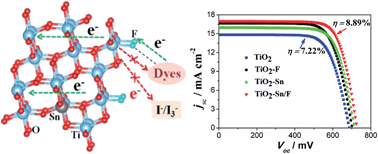
A general strategy to synchronously improve electron transport rate and lifetime for TiO2 photoanode by metal and F− dual doping is proposed and demonstrated for dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) for the first time. Tin and fluorine dual-doped TiO2 nanoparticles are prepared and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis indicates that the Sn atoms and the F atoms locate mainly in the TiO2 lattice and on the TiO2 particles surface, respectively. The DSSC based on Sn/F–TiO2 sample shows a high photoconversion efficiency of 8.89% under an AM 1.5 solar condition (100 mW cm−2), which is higher than those for the undoped TiO2 nanoparticles (7.12%) and the solely Sn (8.14%) or F doped (8.31%) samples. This improvement is attributed to the combined effects of a faster electron transport rate and a longer electron lifetime in the dual-doped TiO2 film. Following this strategy, we also prepare Ta/F, Nb/F, and Sb/F dual-doped TiO2 nanoparticles and find that the performance of DSSCs based on all the dual-doped samples is further improved compared with the single doping cases. Finally, through density functional theory (DFT) calculations, the mechanism behind the improvement by tin and fluorine dual-doping is discussed in detail.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...