Large-scale controllable preparation and performance of hierarchical nickel microstructures by a seed-mediated solution hydrogen reduction route†
Abstract
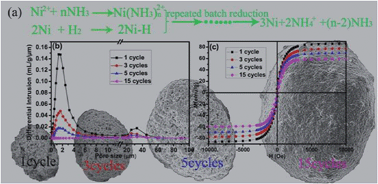
As a part of the persistent efforts to accomplish a sustainable society, solution-hydrogen reduction was developed for preparing metal materials. Large-scale hierarchical nickel microstructures with controllable sizes and pores were constructed by adjusting the reaction conditions and the cycles of repeated reduction using nickel nanoparticles of about 700 nm as seeds and H2 as the reductant. The investigation results of the reaction conditions indicated that ammonia and nickel seeds played crucial roles in the reduction reaction. The possible formation process of self-assembled hierarchical nickel microstructures was proposed based on the results of experiments and analysis. The magnetic hysteresis loops show that the magnetic properties of nickel microstructures were also controllable by controlling the cycles. The hydrogen storage indicates that the hierarchical nickel microstructures have better hydrogen storage performance at 298 K, which may be ascribed reasonably to the H2 molecules that were adsorbed onto the surface of nickel particles and formed activated hydrogen (Ni–H). Such a cost-effective and environmentally friendly procedure is a versatile approach that may be extended to the mass production of some metals and the fabrication of some other hierarchical microstructures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...