Engineering novel polyelectrolyte complex membranes with improved mechanical properties and separation performance†
Abstract
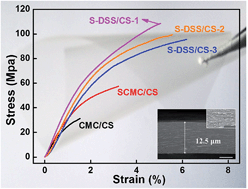
Polyelectrolyte complexes (PECs) commonly suffer from poor processability owing to their ionic crosslinking nature, a problem which spurs increasing interest in processable PECs. New processing technologies have been exploited to render PECs processable, but usually at the expense of compromising their mechanical properties. Through a conceptually novel strategy of “complexation–sulfation”, here we engineer solution-processable PECs derived from a strong polyacid, in pursuit of high mechanical strength combined with exceptional separation performance. Effects of chemical structures and compositions on mechanical properties of these PEC membranes were studied. It was found that the mechanical properties of these PEC membranes based on strong “ion-pairs” were substantially enhanced, with their tensile strength and elongation at break reaching as high as 108.3 MPa and 5.0%, respectively. In addition, PEC membranes exhibited a high performance in separating water–ethanol mixtures. For example, the flux and water content in the permeate for PEC membranes were 2100 g m−2 h−1 and 99.58 wt%, respectively, in dehydrated 10 wt% water–ethanol mixture at 70 °C.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...