Fixing of highly soluble Br2/Br− in porous carbon as a cathode material for rechargeable lithium ion batteries†
Abstract
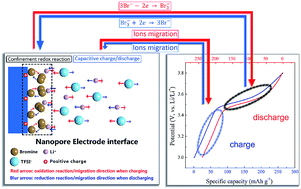
LiBr, as a representative of highly soluble electrochemically active materials, is fixed in nanopores of conductive carbon black (CCB). The Li/LiBr–CCB battery exhibits excellent high-rate capability to avoid slow solid-phase diffusion of Li ions in traditional solid cathode materials. The success will broaden the range of alternative materials for cathodes in LIBs and make them capable of providing both high power density and energy density.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...