Nanosilica/carbon composite spheres as anodes in Li-ion batteries with excellent cycle stability†
Abstract
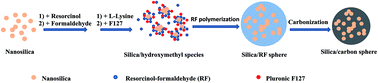
Because of its high capacity, relatively low operation potentials, abundance and environmental benevolence, silica is a promising anode material for high-energy lithium-ion batteries. In this work, to enhance the conductivity of silica and ensure robust connection between silica particles and the host structure in the anode, nanosilica/carbon composite spheres have been fabricated via the in situ copolymerization of formaldehyde and resorcinol on the surface of nanosilica particles, followed by carbonization in an inert atmosphere. The electrochemical properties of the as-prepared composite as an anode for lithium-ion batteries are evaluated. When cycled at a current density of 100 mA g−1 with a voltage window of 0.0–3.0 V the nanosilica/carbon composite spheres present a stable capacity of about 620 mA h g−1 (calculated from the mass of the nanosilica/carbon composite spheres), and the capacity retention is nearly 100% after 300 cycles. Moreover, at different current densities, the as-prepared composite exhibits high capacity and excellent cycle stability. The good electrochemical performance is attributed to the relatively small volume variation of silica nanoparticles, existence of pores/voids in the composite and robust connection between silica nanoparticles and the carbon matrix.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...