Porous nanostructured metal oxides synthesized through atomic layer deposition on a carbonaceous template followed by calcination
Abstract
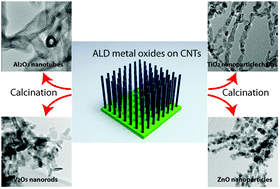
Porous metal oxides with nano-sized features attracted intensive interest in recent decades due to their high surface area which is essential for many applications, e.g. Li ion batteries, photocatalysts, fuel cells and dye-sensitized solar cells. Various approaches have so far been investigated to synthesize porous nanostructured metal oxides, including self-assembly and template-assisted synthesis. For the latter approach, forests of carbon nanotubes are considered as particularly promising templates, with respect to their one-dimensional nature and the resulting high surface area. In this work, we systematically investigate the formation of porous metal oxides (Al2O3, TiO2, V2O5 and ZnO) with different morphologies using atomic layer deposition on multi-walled carbon nanotubes followed by post-deposition calcination. X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy accompanied by X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy were used for the investigation of morphological and structural transitions at the micro- and nano-scale during the calcination process. The crystallization temperature and the surface coverage of the metal oxides and the oxidation temperature of the carbon nanotubes were found to produce significant influence on the final morphology.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...