Hydrothermal synthesis, structure refinement, and electrochemical characterization of Li2CoGeO4 as an oxygen evolution catalyst†
Abstract
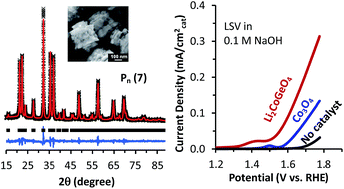
Lithium cobalt germanate (Li2CoGeO4) has been synthesized for the first time by a hydrothermal method at 150 °C. Elemental composition, morphology, and crystal structure of this compound were characterized by various analytical techniques including SEM, TEM, ICP, and XRD analyses. Structure refinement and DFT calculation suggests the crystal structure of the resulting Li2CoGeO4 from hydrothermal synthesis is isostructural to Li2ZnGeO4, significantly different from previous reports. Electrochemical studies confirmed Li2CoGeO4 as an active catalyst for oxygen evolution reaction (OER). In alkaline electrolyte (0.1 M NaOH), rotating disk electrodes made with Li2CoGeO4 as catalyst have a Tafel slope of ca. 67 mV dec−1 and an overpotential of 330 mV at 50 μA cm−2cat, about 90 mV less than the electrodes containing another known OER catalyst, Co3O4. Further characterization with cyclic voltammetry, high resolution transmission electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and elemental analyses revealed the oxidation of Co from 2+ to 3+ during the reaction along with significant surface amorphization and loss of Li and Ge from the catalyst.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...