Amphiphilic superabsorbent cellulose nanofibril aerogels†
Abstract
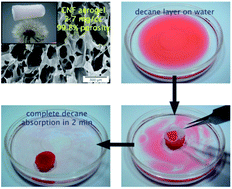
Ultra-light (1.7 to 8.1 mg cm−3) and ultra-porous (99.5 to 99.9%) aerogels have been assembled from cellulose nanofibrils (CNFs) that were defibrillated from rice straw cellulose at 96.8% yield. The as-prepared aerogels, amphiphilic super-absorbents, absorbing 210 and 375 times water and chloroform, respectively, are far superior to any previously reported cellulose aerogel. Vapor deposition with triethoxyl(octyl) silane turned the amphiphilic aerogel more hydrophobic and oleophilic, capable of absorbing 139–356 times non-polar hydrocarbons, polar aprotic solvents and oils, surpassing all previously reported polymeric, cellulosic and carbonaceous aerogels by 2 to nearly 20 times. These aerogels are excellent amphiphilic super-absorbents for selective oil removal and recovery.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...