Enhanced hydrogen desorption of an ammonia borane and lithium hydride system through synthesised intermediate compounds†
Abstract
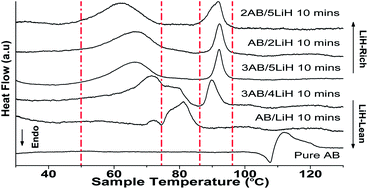
A new hydrogen “storage” strategy is demonstrated for an ammonia borane (AB) and LiH system by means of moderate mechanical milling of the two species under an inert atmosphere. This not only avoids reactive hydrogen release during milling but also leads to formation of an intermediate composite LixNH3−xBH3 (x < 1) to store hydrogen with good stability at ambient temperature. The presence of the intermediate composite and sufficient dispersion of the AB and LiH particles facilitate further reaction of AB and LiH with hydrogen release at a relatively low temperature. Herein, we report a composite system obtained by this simple but effective approach to destabilize AB for enhanced hydrogen release at a desirable temperature. A 10 min milled 3AB/5LiH can release hydrogen of ∼5.3 wt% at 70 °C, and another ∼5.5 wt% at 92 °C; so a total of ∼10.8 wt% hydrogen can be obtained before 92 °C. With an increase of the LiH content, this temperature can be further reduced down to 61 °C, which is a significant improvement that has not been reported before. Moreover, our results show a much lower dehydrogenation temperature, reduced from 92 to 67 °C, and a fast kinetics, e.g., 5 and 9 wt% mass loss at 95 °C within 415 and 1050 s, respectively, which is 6 times faster than those reported in the literature (5 and 9 wt% of mass loss at 100 °C within 2400 and 6900 s, respectively). To the best of our knowledge, our system possesses the highest dehydrogenation capacity (5 wt%) at the low hydrogen release temperature (67 °C), with great improvement on the dehydrogenation kinetics in the solid-state hydride systems. A systemic investigation on the mechanism of the reaction under different milling conditions, reaction temperatures and LiH contents is reported here for the first time.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...