Probing the influence of different oxygenated groups on graphene oxide's catalytic performance†
Abstract
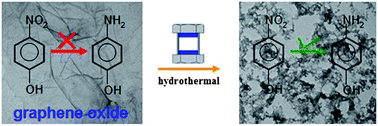
Hydrothermally treated graphene oxide was found to be a new metal-free catalyst for reduction from 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol. Based on the combined experimental and theoretical investigations, hydroxyl and alkoxy radicals, as well as holes were found beneficial to the catalytic performance, while epoxy and carboxyl groups were unfavorable and should be avoided in practical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...