Controllable synthesis of zirconia nano-powders using vapor-phase hydrolysis and theoretical analysis
Abstract
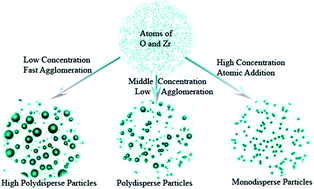
The feasibility of controllable synthesis of nano-crystalline ZrO2 powders using vapor-phase hydrolysis was studied. XRD, SEM, TEM, BET and TG-DTA methods were used to investigate the phase composition, particle size, and agglomeration. The formation process of the nano-particles was also analyzed with the classic Smoluchowski theory, the coupled cluster theory [CCSD(T)]/aT and/or Møller–Plesset perturbation theory (MP2)/aT. The results show that the morphology and size of the ZrO2 nano-particles were very much dependent on the ratio of ZrCl4 : H2O, which played an important part in determining the characteristics of the ZrO2 nano-particles. By increasing the concentration of water to decrease their collision rate and prevent nano-particle agglomeration, the size distribution of the nano-particle product would be decreased and a more monodisperse nano-particle product would be collected. In particular, the best characteristics were obtained using a precursor ratio of 1 : 40 (ZrCl4 : H2O). The nano-powders had a small particle size (15 nm), a high degree of crystallinity and very weak agglomeration, in a continuous instead of batch operation. This route is free of powder drying and calcination processes that are essential for wet chemical preparation, contributing to less agglomeration.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...