Significance of the ZnO nanorod array morphology for low-bandgap polymer solar cells in inverted structures†
Abstract
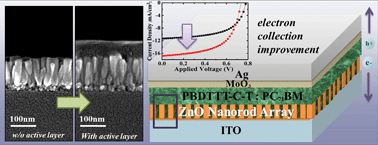
This paper reports an inverted solar cell with ZnO nanorods for electron collection. Because ZnO materials could function as the electron transport layer in inverted organic solar cells, the ZnO nanorods further provided a large number of carrier extraction channels deep inside the organic active layer to improve carrier collection efficiency. The relationship between the ZnO nanorod array morphology and the device performance was systematically studied. Different ZnO nanorod morphologies could be controlled by the ratio of zinc nitrate and hexamethylenetetramine in a low-cost hydrothermal method, including the average spacing between individual nanorods and the surface area. For a maximum organic–inorganic contact area and good polymer infiltration, the morphology of the ZnO nanorod array has been optimized. When the ratio of zinc nitrate and hexamethylenetetramine was controlled at 1.0 : 0.6 in the growth-promoting solution, the surface area of the nanorod array was 7.55 times more than a planar ZnO structure. The ZnO nanorods significantly enhanced the performance of inverted PBDTTT-C-T:PC71BM solar cells and the power conversion efficiency of the device increased from 5.22% to 7.26%.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...