Increase in pore size and gas uptake capacity in indium-organic framework materials†
Abstract
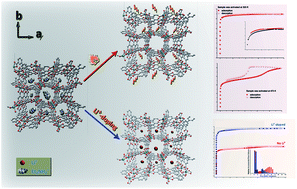
We herein report the synthesis and characterization of a new charged metal-organic framework, [Et2NH2][In(BPTC)] (InOF-2) (InOF = indium-organic framework; BPTC = biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylate), featuring an unc-type topology. Interestingly, InOF-2 undergoes a distinct porosity transition on going from a typical reversible type-I N2 isotherm to a type-IV N2 isotherm with a hysteresis loop when employing thermal treatment. A Li+-exchanged material [Li0.9(H3O)0.1][In(BPTC)] (InOF-2-Li+) is obtained using an ion-exchange method with BET surface areas estimated to be 1494 m2 g−1, and 867 m2 g−1 for InOF-2, indicating that the N2 adsorption capacity of InOF-2-Li+ significantly increases by ca. 72.3%. Meanwhile, H2 adsorption measurements show a corresponding improvement in H2 storage capacity (ca. 70.6%) on going from InOF-2 (1.14 wt%) to desolvated InOF-2-Li+ (1.95 wt%) at 1.0 bar and 77 K, which is comparable to the calculated increase in BET surface area. A similar improvement is also confirmed in other single gas adsorption measurements, including CH4 and CO2. Overall, the performance characteristics of InOF-2 and InOF-2-Li+ indicate these two materials to be unprecedented examples for the charged metal-organic frameworks to improve their gas storage capacity with both the thermal treatment and

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...