Synthesis and characterization of photocrosslinkable albumin-based hydrogels for biomedical applications
Abstract
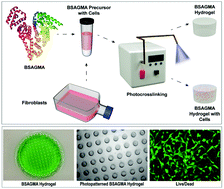
Protein-based biomaterials are widely used to generate three-dimensional (3D) scaffolds for tissue regeneration as well as compact delivery systems for drugs, genes, and peptides. Specifically, albumin-based biomaterials are of particular interest for their ability to facilitate controlled delivery of drugs and other therapeutic agents. These hydrogels possess non-toxic and non-immunogenic properties that are desired in tissue engineering scaffolds. This work employs a rapid ultraviolet (UV) light induced crosslinking to fabricate bovine serum albumin (BSA) hydrogels. Using four different conditions, the BSA hydrogel properties were modulated based on the extent of glycidyl methacrylate modification in each polymer. The highly tunable mechanical behavior of the material was determined through compression tests which yielded a range of material strengths from 4.4 ± 1.5 to 122 ± 7.4 kPa. Pore size measurements also varied from 7.7 ± 1.7 to 23.5 ± 6.6 μm in the photocrosslinked gels. The physical properties of materials such as swelling and degradation were also characterized. In further evaluation, 3D scaffolds were used in cell encapsulation and in vivo implantation studies. The biocompatibility and degradability of the material demonstrated effective integration with the native tissue environment. These modifiable chemical and mechanical properties allow BSA hydrogels to be fine-tuned to a plethora of biomedical applications including regenerative medicine, in vitro cancer study models, and wound healing approaches.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...