A simple and effective strategy to enhance the stability and solid–liquid interfacial interaction of an emulsion by the interfacial dilational rheological properties†
Abstract
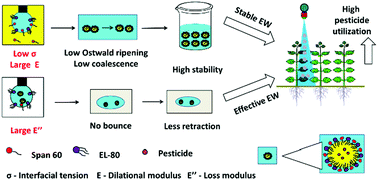
The development of an emulsion is an important challenge in many fields, such as agrochemicals, pharmaceutics, paints, cosmetics, inkjet printing, and food science. However, the traditional strategies that refer to the empirical value and complex secondary additives cannot reflect the influence of the structure, content, compound, and adsorption of emulsifiers. Here, we propose a simple and effective strategy to develop the emulsion, wherein the emulsifiers are chosen based on the dilational rheological properties of the interfacial films at the molecular level. The dilational rheological properties of polyoxyethylene (80) castor oil (EL-80), sorbitan monostearate (Span 60), and their emulsions were explored by the oscillating drop method. Based on the dilational rheological properties, the emulsions were prepared by the phase inversion emulsification technique. The results showed that the emulsion was stable and realized effective solid–liquid interfacial interaction, which was attributed to the large dilational modulus (intermolecular interaction) at the oil/water interface and loss modulus (molecular diffusion exchange) at the air/water interface. These factors reduced the Ostwald ripening and coalescence, and finally increased the spreading diameter. Additionally, the prochloraz 25% emulsion in water (EW) and difenoconazole 20% EW were developed to verify the feasibility of the strategy. Therefore, this research advances the understanding of an emulsion by interfacial dilational rheological properties, which can provide a simple and effective strategy to develop a stable emulsion and achieve an effective solid–liquid interfacial interaction of the emulsion.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...