Shaving and breaking bacterial chains with a viscous flow†
Abstract
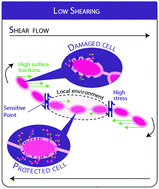
Some food and ferment manufacturing steps such as spray-drying result in the application of viscous stresses to bacteria. This study explores how a viscous flow impacts both bacterial adhesion functionality and bacterial cell organization using a combined experimental and modeling approach. As a model organism we study Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) “wild type” (WT), known to feature strong adhesive affinities towards beta-lactoglobulin thanks to pili produced by the bacteria on cell surfaces, along with three cell-surface mutant strains. Applying repeated flows with high shear-rates reduces bacterial adhesive abilities up to 20% for LGG WT. Bacterial chains are also broken by this process, into 2-cell chains at low industrial shear rates, and into single cells at very high shear rates. To rationalize the experimental observations we study numerically and analytically the Stokes equations describing viscous fluid flow around a chain of elastically connected spheroidal cell bodies. In this model setting we examine qualitatively the relationship between surface traction (force per unit area), a proxy for pili removal rate, and bacterial chain length (number of cells). Longer chains result in higher maximal surface tractions, particularly at the chain extremities, while inner cells enjoy a small protection from surface tractions due to hydrodynamic interactions with their neighbors. Chain rupture therefore may act as a mechanism to preserve surface adhesive functionality in bacteria.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
