Influence of particle size on extraction from a charged bed – toward liquid marble formation†
Abstract
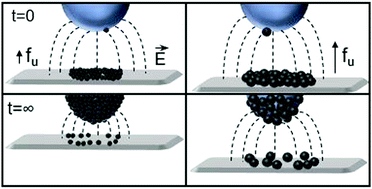
The interactions between particles and the role of their physical properties are not well understood for the electrostatic formation of liquid marbles. Here we focus initially on the impact of increasing particle diameter (notionally 20 to 140 μm) on the ease of particle extraction from an advancing bed of charged particles beneath an earthed, suspended water droplet. A larger particle diameter increased the ease of extraction, due to decreased interparticle cohesion, with increased potential applied to the particle bed. Whilst particle extraction is a crucial step in liquid marble formation, transport to the droplet and subsequent coating and stabilisation of the liquid is also significant. Further investigation highlighted that the smaller particle diameters afforded increased liquid stabilisation due to increased coverage and smaller interstitial spaces between particles on the liquid surface. Optimal conditions for controllable liquid marble formation using electrostatics was postulated as a trade-off between drop-bed separation distance, applied potential and kinetics of coating when studying impact of particle size. Furthermore, preliminary modelling, utilising weakest-link statistics and fracture mechanics, of the experimental data was undertaken to focus on development of the relationship between particle properties and extractability in the presence of electrostatics. This model represents a step towards predicting the suitability of particles for use in the electrostatic formation of liquid marbles prior to undertaking experimental work.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...