Wetting of polymer surfaces by aqueous solutions of branched cationic Gemini surfactants
Abstract
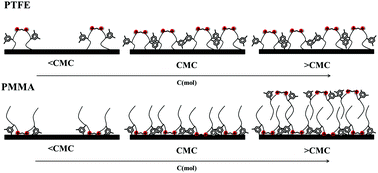
The adsorption of xylyl-substituted biquaternary ammonium salt Gemini surfactants with different spacer (C3 and C6) at polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) surfaces has been investigated and the different adsorption parameters such as surface tension, contact angle, adhesional tension, solid–water interfacial tension and work of adhesion have been estimated. The results show that C3 and C6 have similar adsorption behaviors at PTFE and PMMA surfaces. C3 and C6 adsorb gradually at a PFTE–water interface via hydrophobic interactions and the adsorption amounts at the water–air interface are almost three times higher than those at the PTFE–water interface due to the steric hindrance effect. However, the contact angle keeps constant throughout the experimental concentration range because the decrease in surface tension just counterbalances the decrease in PFTE–water interfacial tension. On the other hand, C3 and C6 adsorb at the PMMA surface via polar interactions between xylyl and functional groups of PMMA before CMC. Similar to PTFE, the increase in PMMA–water interfacial tension compensates the decrease in surface tension and the contact angle also shows a stationary value before the CMC. A bi-layer structure of C3 and C6 will be formed at the PMMA–water interface via hydrophobic interaction and PMMA–water interfacial tension decreases consequently after the CMC, which results in the decrease in contact angle.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...