Rheological behaviour and adsorption phenomenon of a polymer–particle composite based on hydrolysed polyacrylamide/functionalized poly(styrene-acrylic acid) microspheres†
Abstract
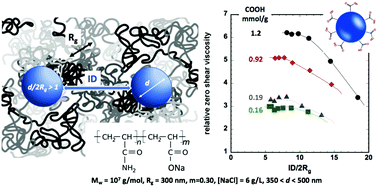
The properties in aqueous solution of polymer–particle composites (PPC) depend on the size and the concentration of both the particles and the polymers as well as the interactions between them. In this work, rheological behaviour was studied in a semi-diluted regime of partially hydrolysed polyacrylamide (HPAM) with 2Rg/d a particle diameter/polymer gyration radius (Rg) ratio and a confinement parameter (pc) that were both greater than 1. Rg is the polymer gyration radius and d the particle diameter. pc characterizes the inter-particle distance (ID) with respect to the polymer size (pc = ID/2Rg) and depends on the concentration and size of the particles. We highlighted the PPC thickening effects as a function of the number of carboxylic functions on the surface of the polystyrene particles (PSL) obtained by free soap free emulsion polymerization (0.16–1.2 mmol g−1 of COOH). Thickening increases linearly with surface functionality for a pc of less than 10. This behaviour has been correlated to the polymer–particle interactions, which was demonstrated by adsorption measurements in dilute solution (12–22 mg g−1 of HPAM on PSL). Adsorption was quantified by zero-shear capillary viscosity measurements in a microfluidic device. In contrast, a thinning effect was observed for a pc greater than 10, which is also related to the salt effect studies (6–12 g L−1 in NaCl).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...