The electric double layer structure modulates poly-dT25 conformation and adsorption kinetics at the cationic lipid bilayer interface†
Abstract
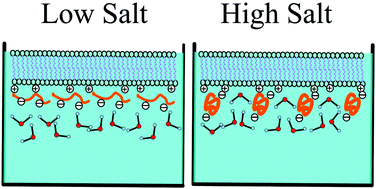
The conformation and adsorption kinetics of oligonucleotides at lipid membrane interfaces are crucial to their biological functions, but are yet not clearly understood. Poly-dT oligonucleotide molecules have been widely used as primers for reverse translation of RNA molecules, as well as a surface recognition agent for mRNA purification and extraction. In this research, the adsorption processes of poly-dT25 on lipid membranes in different ionic solutions were investigated by sum frequency generation vibrational spectroscopy (SFG-VS) together with a single molecule tracking technique in situ and in real time. These systematic studies provide us with molecular insight into the chemical and physical nature of oligonucleotide–membrane interactions, and show us how the electric double layer (EDL) structure changes the conformation and adsorption kinetics of oligonucleotides. The SFG-VS results indicate that an increase of ionic concentration not only decreases the adsorption density of oligonucleotides but also changes the conformation of oligonucleotides from an elongated conformation to a coiled conformation, causing stronger thermodynamic interactions with membranes, as demonstrated by single molecule tracking techniques. It is also shown that the ionic solution can tune the balance between the surface diffusion rate and solution diffusion rate of oligonucleotides significantly. These results demonstrated that the spectra and kinetics collected by in situ label-free SFG-VS detection and the single molecular tracking technique can provide new molecular insights into the mechanisms of oligonucleotide–membrane interactions. These new understandings may help researchers to control the assembly of oligonucleotide–liposome complexes and to improve the efficiency of transportation and delivery of oligonucleotide molecules.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...