Interface structures in ionic liquid crystals
Abstract
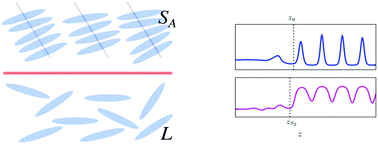
Ionic liquid crystals (ILCs) are anisotropic mesogenic molecules which additionally carry charges. This combination gives rise to a complex interplay of the underlying (anisotropic) contributions to the pair interactions. It promises interesting and distinctive structural and orientational properties to arise in systems of ILCs, combining properties of liquid crystals and ionic liquids. While previous theoretical studies have focused on the phase behavior of ILCs and the structure of the respective bulk phases, in the present study we provide new results, obtained within density functional theory, concerning (planar) free interfaces between an isotropic liquid L and two types of smectic-A phases (SA or SAW). We discuss the structural and orientational properties of these interfaces in terms of the packing fraction profile η(r) and the orientational order parameter profile S2(r) concerning the tilt angle α between the (bulk) smectic layer normal and the interface normal. The asymptotic decay of η(r) and of S2(r) towards their values in the isotropic bulk is discussed, too.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...