Foam drainage placed on a thin porous layer
Abstract
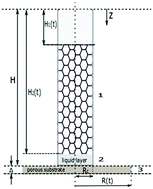
Drainage of foams placed on porous substrates has only recently been theoretically investigated (O. Arjmandi-Tash, N. Kovalchuk, A. Trybala, V. Starov, Foam Drainage Placed on a Porous Substrate, Soft Matter, 2015, 11(18), 3643–3652), where an equation describing foam drainage (with non-slip boundary conditions on the liquid–air interfaces) was combined with that of imbibition of liquid into the thick porous substrate. Foam-based applications have been used as a method of drug delivery, which is a recent and promising area of research related to application of medicinal products onto the skin or hair, which are both thin porous layers. A theory of foam drainage (taking into account surface viscosity) placed on a completely wettable thin porous layer is developed: the rate of foam drainage and imbibition inside the porous layer and other characteristics of the process are predicted. The “effective slip” caused by the surface viscosity increased a movement of the top boundary of the foam. The theoretical predictions are compared with experimental observations of foam drainage placed on thin porous layers. The comparison showed a reasonable agreement between the theoretical predictions and experimental observations. One of the phenomena during foam application is the possibility of a build-up of a free liquid layer on the foam/porous layer interface, which can be very useful for applications. Three different regimes of spreading/imbibition process have been predicted. Conditions and durations of free liquid layer formation have been theoretically predicted and compared with experimental observations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...