Fmoc-FF and hexapeptide-based multicomponent hydrogels as scaffold materials†
Abstract
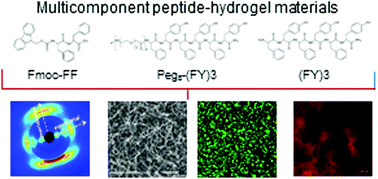
Short peptides or single amino acids are interesting building blocks for fabrication of hydrogels, frequently used as extracellular matrix-mimicking scaffolds for cell growth in tissue engineering. The combination of two or more peptide hydrogelators could allow obtaining different materials exhibiting new architectures, tunable mechanical properties, high stability and improved biofunctionality. Here we report on the synthesis, formulation and multi-scale characterization of peptide-based mixed hydrogels formed by the low molecular weight Fmoc-FF (Nα-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl diphenylalanine) hydrogelator and of the PEG8-(FY)3 hexapeptide, containing three repetitions of the Phe-Tyr motif and a PEG moiety at its N-terminus. Mixed hydrogels were also prepared by replacing PEG8-(FY)3 with its analogue (FY)3, without the PEG moiety. Rheology analysis confirmed the improved mechanical features of the multicomponent gels prepared at two different ratios (2/1 or 1/1, v/v). However, the presence of the hydrophilic PEG polymeric moiety causes a slowing down of the gel kinetic formation (from 42 to 18 minutes) and a decrease of the gel rigidity (G′ from 9 to 6 kPa). Preliminary in vitro biocompatibility and cell adhesion assays performed on Chinese hamster ovarian (CHO) cells suggest a potential employment of these multicomponent hydrogels as exogenous scaffold materials for tissue engineering.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...