Failure mechanisms of coiling fibers with sacrificial bonds made by instability-assisted fused deposition modeling†
Abstract
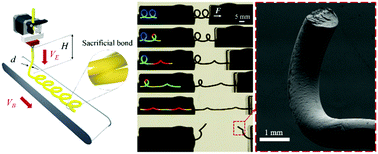
Instability-assisted 3D printing is a method for producing microstructured fibers with sacrificial bonds and hidden lengths that mimic nature's toughening mechanisms found in spider silk. This hierarchical structure increases the effective toughness of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) fibers by 240–340% in some specimens. Nevertheless, many specimens show worse toughness as low as 25% of that of the benchmark straight fiber due to the incomplete release of hidden lengths caused by premature failures. Here, we report the mechanical tests and simulations of microstructured fibers with coiling loops that identify the material plastic deformation as being crucial to fully release the hidden lengths. Without sufficient material yielding, high local tensile stress results from the bending-torsion–tension coupled deformation of the coiling loop and induces crack initiation at the fiber backbone during the loop unfolding process. On the other hand, the influence of bond-breaking defects is found to be negligible here. Moreover, for a number of broken bonds beyond a critical value, the accumulated elastic energy along the released loops induces a high strain rate (∼1500 mm mm−1 s−1) in a quasi-static tensile test, which fractures the fiber backbone within 0.1 ms after the breaking of a new bond. We also show a size effect in fused deposition modeling (FDM) extruded PLA fibers, which results in a higher effective toughness (∼5 times the performance of the straight fiber benchmark) in small coiling fibers (dia. = 0.37 mm), due to the better ductility in bending and torsion compared to large fibers (dia. = 1.20 mm). The failure mechanisms of single microstructured fibers presented here lay the groundwork for further optimizations of fiber arrays in the next generation of high energy-absorption composites for impact protection and safety-critical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...