Liquid–liquid phase equilibrium and the effect of a water-soluble polymer on the interaction between droplets in water-in-oil microemulsions†
Abstract
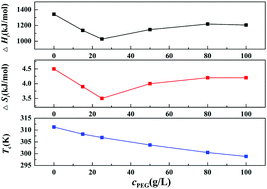
The liquid–liquid phase equilibria of {water/PEG200/sodium bis(2-ethylhexyl)sulfosuccinate (AOT)/n-decane} with the molar ratio of water to AOT being 37.9 and various concentrations cPEG of PEG in water were measured in this study. The critical exponent β corresponding to the width of the coexistence curve was determined, which showed good agreement with the 3D-Ising value and supported the proposal of the pseudo binary droplet solution for these multiple microemulsions. A previously developed thermodynamic approach based on the Carnahan–Starling–van der Waals type equation was improved and used to analyze the coexistence curve data of {water/PEG200/AOT/n-decane} microemulsions to deduce the interaction properties between droplets and further to investigate the effect of the additive PEG200 on these interactions. It was found that the addition of PEG200 into the {water/AOT/n-decane} microemulsion resulted in the decrease in the critical temperature and the interaction enthalpy and entropy. Both the interaction enthalpy and entropy decreased first, then increased with an increase of cPEG and had minimum values at cPEG = 25 g L−1, which showed the same tendency as the isothermal titration microcalorimetric results for the {water/PEG200/AOT/isooctane} microemulsion we reported very recently. The effects of the interaction enthalpy and the entropy on the phase separation and their dependences on cPEG were discussed and related to the effects of the additive on the rigidity of the interface layer of the microemulion droplet.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...