Colloidal stability dictates drop breakup under electric fields†
Abstract
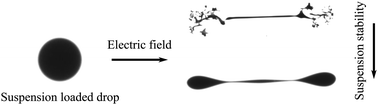
Electric fields can deform drops of fluid from their equilibrium shape, and induce breakup at sufficiently large field strengths. In this work, the electric field induced breakup of a squalane drop containing a colloidal suspension of carbon black particles with polyisobutylene succinimide (OLOA 11000) surfactant is studied. The drop is suspended in silicone oil. The breakup mode of a drop containing carbon black depends strongly on the suspension stability. It is observed that a drop of a stable suspension of carbon black has the same breakup mode as a drop with surfactant alone, i.e., without added carbon black. At lower electric fields, these drops break by the formation of lobes at the two ends of the drop; and at higher fields the homogeneous lobes break in a non-axisymmetric manner. However, a drop of an unstable suspension shows a drastically different breakup mode, and undergoes breakup much faster compared to a drop with surfactant alone. These drops elongate and form asymmetric lobes that develop into fingers and eventually disintegrate in an inhomogeneous, three-dimensional fashion. As a basis for comparison, the breakup of a pure squalane drop, and a squalane drop with equivalent surfactant concentrations but no carbon black particles is examined. Axisymmetric boundary integral computations are used to elucidate the mechanism of breakup. Our work demonstrates the impact of colloidal stability on the breakup of drops under an electric field. Colloidal stability on the time scale of drop deformation leads to rich and unexplored breakup phenomena.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
