Formation of lipid vesicles in situ utilizing the thiol-Michael reaction†
Abstract
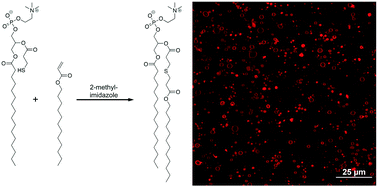
Synthetic unilamellar liposomes, functionalized to enable novel characteristics and behavior, are of great utility to fields such as drug delivery and artificial cell membranes. However, the generation of these liposomes is frequently highly labor-intensive and time consuming whereas in situ liposome formation presents a potential solution to this problem. A novel method for in situ lipid formation is developed here through the covalent addition of a thiol-functionalized lysolipid to an acrylate-functionalized tail via the thiol-Michael addition reaction with potential for inclusion of additional functionality via the tail. Dilute, stoichiometric mixtures of a thiol lysolipid and an acrylate tail reacted in an aqueous media at ambient conditions for 48 hours reached nearly 90% conversion, forming the desired thioether-containing phospholipid product. These lipids assemble into a high density of liposomes with sizes ranging from 20 nm to several microns in diameter and include various structures ranging from spheres to tubular vesicles with structure and lamellarity dependent upon the catalyst concentration used. To demonstrate lipid functionalization, an acrylate tail possessing a terminal alkyne was coupled into the lipid structure. These functionalized liposomes enable photo-induced polymerization of the terminal alkyne upon irradiation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
