Co-assemblies of polydiacetylenes and metal ions for solvent sensing†
Abstract
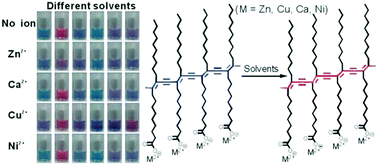
We demonstrate an easy and low-cost approach for the colorimetric differentiation of organic solvents using co-assemblies of polydiacetylenes (PDAs) and metal ions. The co-assemblies were prepared by the self-assembly of amphiphilic 10,12-tricosa diynoic acid with different metal ions (Zn2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, Ca2+) and subsequent photopolymerization. Different metal ions underwent different interactions with the carboxyl groups on the side chains of poly(10,12-tricosa diynoic acid), which influenced the stimuli-responsiveness of the PDA/metal ion co-assemblies. As a result, the PDA/metal ion co-assemblies with different metal ions showed different solvatochromism. Based on this property, the co-assemblies were used as sensors to differentiate organic solvents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...