Tuneable spheroidal hydrogel particles for cell and drug encapsulation
Abstract
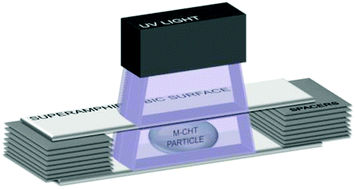
The need to better mimic native tissues has accompanied research in tissue engineering and controlled drug delivery. The development of new platforms for cell and drug encapsulation followed the same trend, and studying the influence of the delivery material system's geometry has been gaining momentum. Aiming to investigate how an increase in surface area and varying particle shape could impact drug release and cell viability, a novel method was developed to produce spheroidal hydrogel particles with adjustable circularity, aiming to tune drug delivery. For this purpose, droplets of hydrogel precursor were squeezed between two superamphiphobic surfaces separated with spacers with different height, and then photo-crosslinked to maintain the acquired shape after “de-sandwiching”. Numerical modelling studies were performed to study the polymeric droplet geometry deformation process, which were consistent with experimentally obtained results. The spheroidal particles were produced under mild conditions using methacrylated chitosan, capable of encapsulating proteins or cells. Likely due to their higher surface area to volume-ratio, compared to spherical-shaped ones, spheroids presented an improved viability of encapsulated cells due to enhanced nutrient diffusion to the core, and led to a significantly faster drug release rate from the polymer network. These results were also assessed numerically, in which the drug release rate was computed for different spheroidal-like geometries. Hence, the described method can be used to manufacture spheroidal particles with tailored geometry that can be broadly applied in the biomedical field, including for drug delivery or as cell encapsulation platforms.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...