Towards optimised drug delivery: structure and composition of testosterone enanthate in sodium dodecyl sulfate monolayers†
Abstract
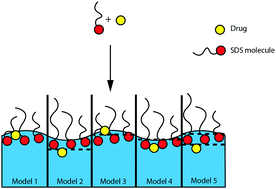
Surface tension and specular neutron reflectivity measurements have been used, for the first time to systematically study both the interfacial structure and composition of monolayers of the soluble surfactant, sodium dodecyl sulfate containing a low-dose, poorly water soluble drug, testosterone enanthate. Modelling of the specular neutron reflectivity data suggests that the hydrophobic testosterone enanthate was adsorbed in the C12 hydrophobic tail region of the surfactant monolayer, regardless of the concentration of surfactant at the interface and whether or not additional drug was added to the interface. The location of the hydrophobic drug in the tail region of the surfactant monolayer is supported by the results of classical, large-scale molecular dynamics simulations. The thickness of the surfactant monolayer obtained, in the presence and absence of drug, using molecular dynamics simulations was in good agreement with the corresponding values obtained from the specular neutron reflectivity measurements. The stoichiometry of surfactant:drug at the air–water interface at sodium dodecyl sulfate concentrations above the critical micelle concentration was determined from specular neutron reflectivity measurements to be approximately 3 : 1, and remained constant after the spreading of further testosterone enanthate at the interface. Significantly, this stoichiometry was the same as that obtained in the micelles from bulk solubilisation studies. Important insights into the preferred location of drug in surfactant monolayers at the air–water interface as well as its effect on the structure of the monolayer have been obtained from our combined use of experimental and simulation techniques.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...