Lysine-derived, pH-sensitive and biodegradable poly(beta-aminoester urethane) networks and their local drug delivery behaviour†
Abstract
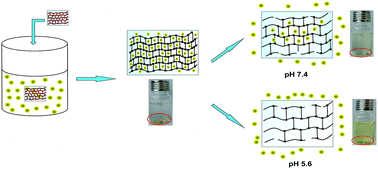
In this study, a series of covalently crosslinked, L-lysine based poly(beta-aminoester urethane) (LPBAEU) networks with good biodegradability and pH sensitivity was reported. The effect of hydrophilic/hydrophobic characteristics and diacrylate/amine molar ratio on the structure, swelling and degradation behaviour of the networks was investigated. The water transport mechanism and dynamic swelling behavior of the LPBAEU networks were strongly affected by medium pH, and swelling amounts up to 252.2% and 148.7% were observed at pH 5.6 and pH 7.4, respectively. It was found that water diffusion within the networks followed a non-Fickian mechanism. The LPBAEU network with the highest diacrylate/amine molar ratio exhibited the highest tensile strength and Young's modulus. In vitro mass losses of networks showed that the degradation rate of LPBAEU networks can be adjusted from 4 to 14 days. LPBAEU networks also supported loading of doxycycline hyclate (DH) and in vitro release studies demonstrated that release of DH from the networks was substantially hindered in the neutral pH environment, with 20.9–56.2% DH release, whereas DH release was accelerated under mild acidic conditions, with a release percentage of 36.6–99.6%. The release data were fitted to different mathematical models and the obtained results confirmed that these networks released DH in a non-Fickian mechanism. The results of this research support the idea that pH-responsive LPBAEU networks may find potential applications in local drug delivery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...