Silk nanoparticles: from inert supports to bioactive natural carriers for drug delivery
Abstract
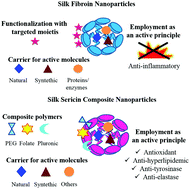
Silk proteins have been studied and employed for the production of drug delivery (nano)systems. They show excellent biocompatibility, controllable biodegradability and non-immunogenicity and, if needed, their properties can be modulated by blending with other polymers. Silk fibroin (SF), which forms the inner core of silk, is a (bio)material officially recognized by the Food and Drug Administration for human applications. Conversely, the potential of silk sericin (SS), which forms the external shell of silk, could still be considered under evaluation. At the best of our knowledge, nanoparticles based on silk sericin “alone” cannot be produced, due to its physicochemical instability influenced by extreme pH, high water solubility and temperature; for these reasons, it almost always needs to be combined with other polymers for the development of drug delivery systems. In this review, we focused on silk proteins as bioactive natural carriers, since they show not only optimal features as inert excipients, but also remarkable intrinsic biological activities. SF has anti-inflammatory properties, while SS presents antioxidant, anti-tyrosine, anti-aging, anti-elastase and anti-bacterial features. Here, we give an overview on SF or SS silk-based nanosystems, with particular attention on the production techniques.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...