Nanoscopic dynamics of bicontinous microemulsions: effect of membrane associated protein
Abstract
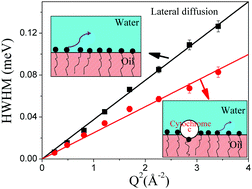
Bicontinous microemulsions (BμE) generally consist of nanodomains formed by surfactant in a mixture of water and oil at nearly equal proportions and are potential candidates for the solubilization and purification of membrane proteins. Here we present the first time report of nanoscopic dynamics of surfactant monolayers within BμEs formed by the anionic surfactant sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) measured on the nanosecond to picosecond time scale using quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS). BμEs investigated herein consisted of middle phases isolated from Winsor-III microemulsion systems that were formed by mixing aqueous and oil solutions under optimal conditions. QENS data indicates that surfactants undergo two distinct motions, namely (i) lateral motion along the surface of the oil nanodomains and (ii) localized internal motion. Lateral motion can be described using a continuous diffusion model, from which the lateral diffusion coefficient is obtained. Internal motion of surfactant is described using a model which assumes that a fraction of the surfactants’ hydrogens undergoes localized translational diffusion that could be considered confined within a spherical volume. The effect of cytochrome c, an archetypal membrane-associated protein known to strongly partition near the surfactant head groups in BμEs (a trend supported by small-angle X-ray scattering [SAXS] analysis), on the dynamics of BμE has also been investigated. QENS results demonstrated that cytochrome c significantly hindered both the lateral and the internal motions of surfactant. The lateral motion was more strongly affected: a reduction of the lateral diffusion coefficient by 33% was measured. This change is mainly attributable to the strong association of cytochrome c with oppositely charged SDS. In contrast, analysis of SAXS data suggested that thermal fluctuations (for a longer length and slower time scale compared to QENS) were increased upon incorporation of cytochrome c. This study demonstrates the utility of QENS for evaluating dynamics of BμEs in nanoscopic region, and that proteins directly affect the microscopic dynamics, which is of relevance for evaluating release kinetics of encapsulated drugs from BμE delivery systems and the use of BμEs as biomembrane mimetic systems for investigating membrane protein–biomembrane interactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...