Interfacial rheology of polymer/carbon nanotube films co-assembled at the oil/water interface†
Abstract
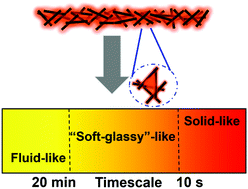
At appropriate conditions, water-dispersed acid-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) co-assemble at the oil/water interface with toluene-dissolved amine-terminated polystyrene (PS-NH2) to form composite thin films displaying pronounced interfacial viscoelasticity. To probe this viscoelasticity, the films were examined under dilatational deformations of pendant drop tensiometry/rheometry, with storage and loss moduli recorded against frequency ω (0.003 < ω < 3 Hz) and time-dependent relaxation modulus recorded against time t (0.2 < t < 2000 s). Without the SWCNTs, PS-NH2-decorated interfaces have little dilatational stiffness, i.e., low storage modulus, but their stiffness grows as SWCNTs are added, reaching 50–100 mN m−1 at large ω. Two characteristic relaxation processes are identified in the composite films: a fast process (ω ∼ 0.1–0.2 Hz) attributable to local structural relaxation of confined PS-NH2 and a slow process (t ∼ 300–2000 s) attributable to component adsorption/desorption (or attachment/detachment). Among the variables that affect positions and strengths of these relaxations are SWCNT and PS-NH2 bulk concentrations as well as water phase pH. In frequency or timescale ranges intermediate between the two relaxations, the co-assembled films display “soft-glass” behavior, with the storage and loss moduli characterized by nearly equal power-law exponents. The relaxation modulus, better able to probe terminal behavior, eventually decays to zero, revealing that the films are fundamentally fluid-like due to the slow relaxation, and in support of this conclusion, large strain compression-induced film wrinkles disappear at large t.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...