Induced smectic phases of stoichiometric liquid crystal mixtures
Abstract
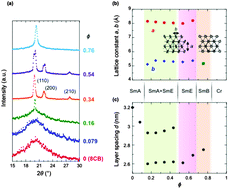
We revealed the detailed structures of induced smectic liquid crystal (LC) phases composed of a binary mixture of charge-transfer (CT) LC substances. Although neither of the constituents had highly ordered smectic phases, the mixture exhibited smectic-E (SmE) or smectic-B (SmB) phases when mixed at ratios of 1 : 1 and 2 : 3, respectively. The results of polarized optical microscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray diffraction, and infrared spectroscopy indicated that the induced smectic phases were stabilized by an exquisite balance between the CT interactions, dipolar interactions, and excluded volume effects. We proposed a possible model for the molecular arrangements in the SmE and SmB phases, which consistently explained the experimental results including the stoichiometric ratios.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...