Structure and cohesive energy of dipolar helices
Abstract
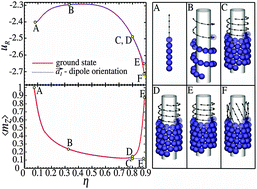
This paper deals with the investigation of cohesive energy in dipolar helices made up of hard spheres. Such tubular helical structures are ubiquitous objects in biological systems. We observe a complex dependence of cohesive energy on surface packing fraction and dipole moment distribution. As far as single helices are concerned, the lowest cohesive energy is achieved at the highest surface packing fraction. Besides, a striking non-monotonic behavior is reported for the cohesive energy as a function of the surface packing fraction. For multiple helices, we discover a new phase, exhibiting markedly higher cohesive energy. This phase is referred to as ZZ tube consisting of stacked crown rings (reminiscent of a pile of zig-zag rings), resulting in a local triangular arrangement with densely packed filaments parallel to the tube axis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...