Stochastic binding of Staphylococcus aureus to hydrophobic surfaces†
Abstract
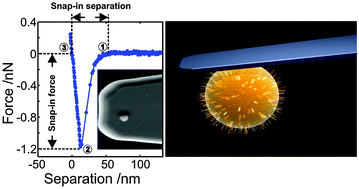
The adhesion of pathogenic bacteria to surfaces is of immense importance for health care applications. Via a combined experimental and computational approach, we studied the initiation of contact in the adhesion process of the pathogenic bacterium Staphylococcus aureus. AFM force spectroscopy with single cell bacterial probes paired with Monte Carlo simulations enabled an unprecedented molecular investigation of the contact formation. Our results reveal that bacteria attach to a surface over distances far beyond the range of classical surface forces via stochastic binding of thermally fluctuating cell wall proteins. Thereby, the bacteria are pulled into close contact with the surface as consecutive proteins of different stiffnesses attach. This mechanism greatly enhances the attachment capability of S. aureus. It, however, can be manipulated by enzymatically/chemically modifying the cell wall proteins to block their consecutive binding. Our study furthermore reveals that fluctuations in protein density and structure are much more relevant than the exact form of the binding potential.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...