Colloid-probe AFM studies of the interaction forces of proteins adsorbed on colloidal crystals
Abstract
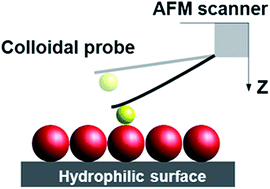
In recent years, colloid-probe AFM has been used to measure the direct interaction forces between colloidal particles of different size or surface functionality in aqueous media, as one can study different forces in symmerical systems (i.e., sphere–sphere geometry). The present study investigates the interaction between protein coatings on colloid probes and hydrophilic surfaces decorated with hexagonally close packed single particle layers that are either uncoated or coated with proteins. Controlled solvent evaporation from aqueous suspensions of colloidal particles (coated with or without lysozyme and albumin) produces single layers of close-packed colloidal crystals over large areas on a solid support. The measurements have been carried out in an aqueous medium at different salt concentrations and pH values. The results show changes in the interaction forces as the surface charge of the unmodified or modified particles, and ionic strength or pH of the solution is altered. At high ionic strength or pH, electrostatic interactions are screened, and a strong repulsive force at short separation below 5 nm dominates, suggesting structural changes in the absorbed protein layer on the particles. We also study the force of adhesion, which decreases with an increment in the salt concentration, and the interaction between two different proteins indicating a repulsive interaction on approach and adhesion on retraction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...