Redox control of GPx catalytic activity through mediating self-assembly of Fmoc-phenylalanine selenide into switchable supramolecular architectures†
Abstract
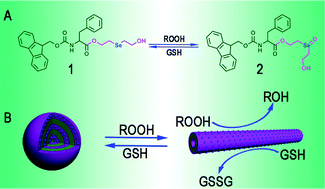
Artificial enzymes capable of achieving tunable catalytic activity through stimuli control of enzymatic structure transition are of significance in biosensor and biomedicine research. Herein we report a novel smart glutathione peroxidise (GPx) mimic with modulatory catalytic activity based on redox-induced supramolecular self-assembly. First, an amphiphilic Fmoc-phenylalanine-based selenide was designed and synthesized, which can self-assemble into nanospheres (NSs) in aqueous solution. The NSs demonstrate extremely low GPx activity. Upon the oxidation of hydroperoxides (ROOH), the selenide can be quickly transformed into the selenoxide form. The change of the molecular structure induces complete morphology transition of the self-assemblies from NSs to nanotubes (NTs), resulting in great enhancement in the GPx catalytic activity. Under the reduction of GSH, the selenoxide can be further reversibly reduced back into the selenide; therefore the reversible switch between the NSs and NTs can be successfully accomplished. The relationship between the catalytic activity and enzymatic structure was also investigated. The dual response nature makes this mimic play roles of both a sensor and a GPx enzyme at the same time, which can auto-detect the signal of ROOH and then auto-change its activity to achieve quick or slow/no scavenging of ROOH. The dynamic balance of ROOH is vital in organisms, in which an appropriate amount of ROOH does benefit to the metabolism, whereas surplus ROOH can cause oxidative damage of the cell instead and this smart mimic is of remarkable significance. We expect that such a mimic can be developed into an effective antioxidant drug and provide a new platform for the construction of intelligent artificial enzymes with multiple desirable properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...