Oil-in-water microemulsion droplets of TDMAO/decane interconnected by the telechelic C18-EO150-C18: clustering and network formation†
Abstract
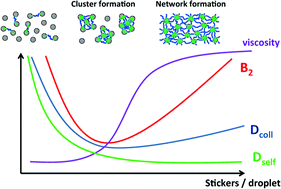
The effect of a doubly hydrophobically end-capped water soluble polymer (C18-PEO150-C18) on the properties of an oil-in-water (O/W) droplet microemulsion (R ∼ 2.85 nm) has been studied as a function of the amount of added telechelic polymer. Macroscopically one observes a substantial increase of viscosity once a concentration of ∼5 hydrophobic stickers per droplet is surpassed and effective cross-linking of the droplets takes place. SANS measurements show that the size of the individual droplets is not affected by the polymer addition but it induces attractive interactions at low concentration and repulsive ones at high polymer content. Measurements of the diffusion coefficient by DLS and FCS show increasing sizes at low polymer addition that can be attributed to the formation of clusters of microemulsion droplets interconnected by the polymer. At higher polymer content the network formation leads to an additional slow relaxation mode in DLS that can be related to the rheological behaviour, while the self-diffusion observed in FCS attains a lower plateau value, i.e., the microemulsion droplets remain effectively fixed within the network. The combination of SANS, DLS, and FCS allows us to derive a self-consistent picture of the evolution of structure and dynamics of the mixed system microemulsion/telechelic polymer as a function of the polymer content, which is not only relevant for controlling the macroscopic rheological properties but also with respect to the internal dynamics as it is, for instance, relevant for the release and transport of active agents.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...