Collapse from the top: brushes of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) in co-nonsolvent mixtures†
Abstract
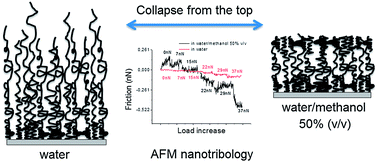
Using a combination of ellipsometry and friction force microscopy, we study the reversible swelling, collapse and variation in friction properties of covalently bound poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) layers on silicon with different grafting densities in response to exposure to good solvents and co-nonsolvent mixtures. Changes in the thickness and segment density distribution of grafted films are investigated by in situ ellipsometry. Based on quantitative modelling of the ellipsometry spectra, we postulate a structural model, which assumes that collapse takes place in the contacting layer between the brush and the co-nonsolvent and the top-collapsed brushes remain hydrated in the film interior. Using the structural model derived from ellipsometry spectra, we analyse the AFM based friction force microscopy data, which were obtained by silica colloidal probes. Results show a large increase of the friction coefficient of PNIPAM grafts when the grafts swollen by water are brought in contact with co-nonsolvents. For instance, the value of the friction coefficient for a medium density brush in water is four times lower than the value observed in a water–methanol (50% v/v) mixture. This increase of friction is accompanied by an increase in adherence between the PNIPAM chains and the silica colloidal probes, and is a result of chain collapse in the graft when contacted by a co-nonsolvent mixture in agreement with the model postulated on the basis of ellipsometric characterisation. The kinetic behaviour of the collapse is assessed by measuring the temporal variation of friction in situ as a function of elapsed time following contact with the co-nonsolvent as a function of graft density. In conclusion, the effect of co-nonsolvency influenced both the thickness of the PNIPAM brushes and the tribological behavior of the brush surfaces.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...