Nanomechanical response of bacterial cells to cationic antimicrobial peptides†
Abstract
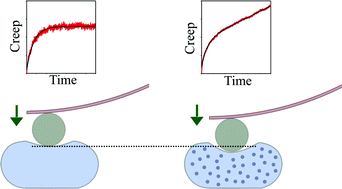
The effectiveness of antimicrobial compounds can be easily screened, however their mechanism of action is much more difficult to determine. Many compounds act by compromising the mechanical integrity of the bacterial cell envelope, and our study introduces an AFM-based creep deformation technique to evaluate changes in the time-dependent mechanical properties of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 bacterial cells upon exposure to two different but structurally related antimicrobial peptides. We observed a distinctive signature for the loss of integrity of the bacterial cell envelope following exposure to the peptides. Measurements performed before and after exposure, as well as time-resolved measurements and those performed at different concentrations, revealed large changes to the viscoelastic parameters that are consistent with differences in the membrane permeabilizing effects of the peptides. The AFM creep deformation measurement provides new, unique insight into the kinetics and mechanism of action of antimicrobial peptides on bacteria.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Interaction of nano-objects with lipid membranes
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...